Basics
Stock Market
causes of COVID-19 market crash, COVID-19 stock market crash 2020, financial crisis COVID-19 vs 2008, global stock market crash COVID-19, how COVID affected stock market worldwide, impact of coronavirus on stock market, investor psychology during COVID-19 crash, lessons from 2020 stock market crash, March 2020 market crash explained, pandemic impact on global economy and markets, stock market crash history 2020, stock market investing lessons from COVID-19, stock market recovery after COVID crash, stock market volatility during pandemic
bullbearfin
0 Comments
COVID-19 Pandemic Crash (March 2020): Causes, Impact, and Lessons for Investors
Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic was not only a global health crisis but also one of the most devastating shocks to the global financial system in modern history. In March 2020, as the virus spread uncontrollably across countries, governments imposed lockdowns, international trade slowed, businesses closed, and uncertainty gripped investors. Within days, global stock markets crashed, wiping out trillions of dollars in market capitalization.
This article provides an in-depth exploration of the March 2020 crash, covering its causes, timeline, global market reactions, investor psychology, recovery patterns, and the valuable lessons it taught to traders, investors, and policymakers.
1. Background: COVID-19 and Early Signs of Trouble
The COVID-19 virus was first reported in late December 2019 in Wuhan, China. At the time, markets largely ignored the news, assuming it would remain a local health crisis.
- January 2020 – Chinese markets showed early volatility due to city lockdowns.
- February 2020 – As the virus spread globally, supply chains faced disruptions. Companies like Apple, Tesla, and automakers warned of production issues.
- Despite warning signs, U.S. and European markets still traded near all-time highs until mid-February 2020.
This set the stage for a sudden and sharp collapse once the reality of the pandemic became undeniable.
2. The March 2020 Crash: Timeline of Events
📆 February 19, 2020 – Market Peak
- U.S. stock markets hit record highs (S&P 500 at 3,386).
- Investor optimism ignored virus risks.
📆 February 24–28, 2020 – First Wave of Panic
- Italy announced nationwide lockdowns.
- Global markets lost $6 trillion in a week.
- Dow Jones Industrial Average fell 3,500 points in five days.
📆 March 9, 2020 – “Black Monday”
- Dow Jones fell 2,013 points (7.8%) in one day.
- Oil price war (Saudi Arabia vs. Russia) worsened panic.
📆 March 12, 2020 – “Black Thursday”
- S&P 500 crashed 9.5%, biggest single-day fall since 1987.
- European markets collapsed 11–12%.
- Investors fled to cash and gold.
📆 March 16, 2020 – “Black Monday II”
- Dow plunged 2,997 points (12.9%), largest one-day point drop ever.
- Circuit breakers were triggered multiple times in March.
📆 March 23, 2020 – Market Bottom
- S&P 500 fell 34% from its peak within one month.
- Global stock markets collectively lost $20 trillion in value.
3. Causes of the COVID-19 Market Crash
The March 2020 crash was triggered by a perfect storm of events:
- Pandemic Uncertainty – No vaccine, no cure, and rising death rates created fear.
- Global Lockdowns – Businesses, airlines, hospitality, and retail sectors shut down.
- Oil Price War – Saudi Arabia and Russia flooded markets with cheap oil, collapsing crude prices to below $20.
- Investor Panic – Herd behavior led to mass sell-offs.
- Debt Concerns – Corporate debt levels were already high, making investors worry about defaults.
- Supply Chain Disruptions – China’s lockdown halted global manufacturing.
4. Impact on Global Stock Markets
🇺🇸 United States
- Dow Jones lost 10,000+ points in March 2020.
- S&P 500 plunged over 30% from highs.
- Nasdaq also crashed but recovered faster due to tech stocks.
🇪🇺 Europe
- FTSE 100 (UK) lost 25%.
- German DAX fell nearly 30%.
- Travel and hospitality sectors were hardest hit.
🇨🇳 China
- Shanghai Composite fell but recovered earlier due to faster containment measures.
🇮🇳 India
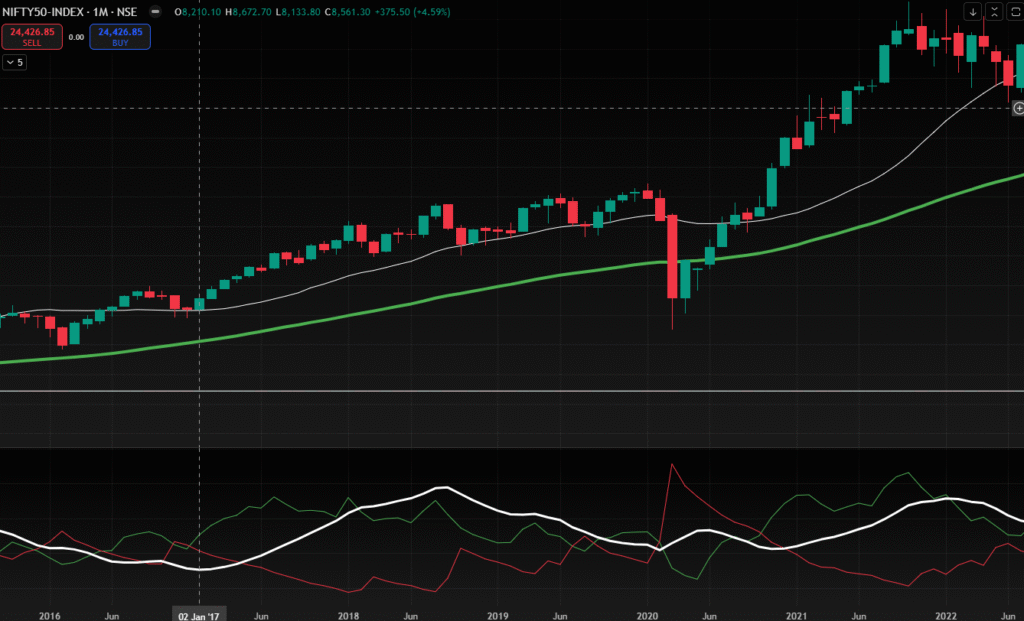
- Nifty 50 fell 38%, hitting 7,500 levels from above 12,000.
- Foreign investors pulled out billions, weakening the rupee.
🌍 Global
- Oil prices crashed below $0 (negative pricing) in April 2020 futures contracts.
- Gold surged as a safe-haven asset.
- Emerging markets saw massive capital outflows.
5. Investor Psychology During the Crash
Investor behavior played a huge role in accelerating the March 2020 crash:
- Fear & Panic Selling – Investors liquidated portfolios to hold cash.
- Herd Mentality – Selling pressure spread like wildfire across the globe.
- Flight to Safety – Gold, U.S. Treasuries, and cash saw inflows.
- Short-Term Thinking – Even long-term investors panicked and sold at lows.
This was a classic case of the “Fear and Greed Index” swinging entirely towards fear.
6. Government and Central Bank Interventions
Governments and central banks took unprecedented steps to stabilize markets:
- U.S. Federal Reserve
- Cut interest rates to near zero.
- Launched unlimited quantitative easing (QE).
- Introduced liquidity programs for corporations.
- European Central Bank (ECB)
- Announced €750 billion bond-buying program.
- Indian Government & RBI
- Announced ₹20 lakh crore economic package.
- Moratoriums on loan repayments.
- Liquidity support for NBFCs and banks.
These measures restored confidence and triggered the fastest stock market recovery in history.
7. The Recovery Phase
- April–June 2020 – Markets rebounded sharply due to stimulus measures.
- Tech Stocks Boom – Work-from-home trends boosted companies like Zoom, Microsoft, Amazon.
- Vaccine News (Late 2020) – Sparked a global bull run.
- By August 2020, markets regained pre-COVID levels.
- By 2021, many indices hit new all-time highs, proving the resilience of markets.
8. Lessons from the COVID-19 Crash
- Markets Can Crash Fast – 34% fall in just one month.
- Stay Invested – Those who sold in panic missed one of the strongest recoveries.
- Diversification Matters – Balanced portfolios did better than concentrated bets.
- Cash is King – Liquidity gave investors flexibility during uncertainty.
- Behavioral Discipline – Controlling fear and sticking to a plan is key.
- Follow Central Banks – Stimulus policies often determine recovery speed.
9. Comparison with Past Crashes
- 1929 Great Depression – Took years to recover.
- 2008 Global Financial Crisis – Recovery took 4+ years.
- 2020 COVID Crash – Recovery within 6 months, fastest in history.
10. Conclusion
The COVID-19 Pandemic Crash of March 2020 was one of the sharpest and most frightening collapses in stock market history. Yet, it also became a remarkable example of resilience, showing how markets, economies, and investors adapt to crises.
For traders and investors, it reinforced the importance of:
- Maintaining discipline,
- Managing risk,
- Staying diversified,
- And most importantly, controlling emotions in times of uncertainty.
The COVID crash will be remembered not only as a financial disaster but also as a powerful lesson in market psychology and global interconnectedness.
Top 5 Options Trading Strategies for Beginners
Common Mistakes in Futures & Options Trading

Post Comment