Bear Put Spread Strategy Explained
Options trading offers flexibility for both bullish and bearish outlooks. While bullish traders use strategies such as the Bull Call Spread, bearish traders can rely on the Bear Put Spread.
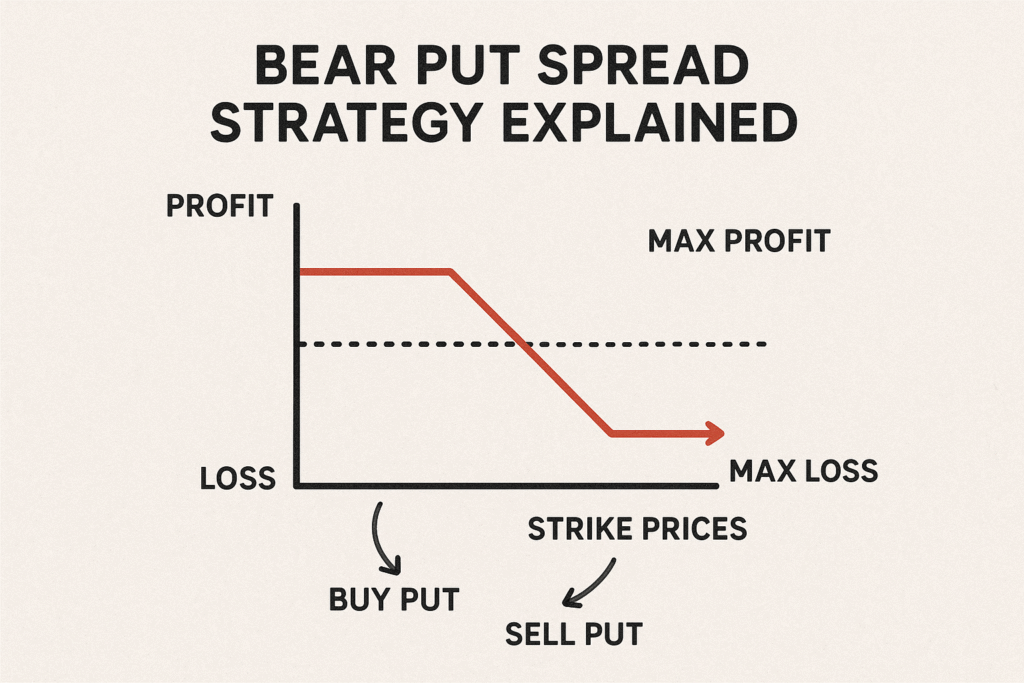
This strategy is widely used when a trader has a moderately bearish view on a stock or index. It allows participation in downside moves while limiting risk and reducing the upfront cost compared to simply buying a put option.
In this detailed guide, we will cover:
- What the Bear Put Spread strategy is
- How it works
- When to use it
- Payoff structure and calculations
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Practical examples (both stock and index)
- Key tips for traders
1. What is a Bear Put Spread?
A Bear Put Spread is a bearish options trading strategy that involves:
- Buying a Put Option at a Higher Strike Price (ATM or ITM).
- Selling a Put Option at a Lower Strike Price (OTM) with the same expiry.
📌 Key Idea:
- You profit when the stock falls.
- Selling the lower strike put reduces the total premium paid.
- But it also caps your maximum profit.
In essence, it’s a cost-effective alternative to buying a naked put, ideal for traders who expect moderate downside but not a market crash.
2. When Should You Use a Bear Put Spread?
The Bear Put Spread is best suited when:
- You are moderately bearish on a stock/index.
- You expect a limited decline in price.
- You want to reduce the premium cost compared to naked put buying.
Examples of situations:
- Before earnings announcements when weak results are expected.
- In a weak market trend where stocks are falling slowly.
- During uncertain periods when you want defined risk.
3. How Does a Bear Put Spread Work?
Let’s break down the steps:
- Buy a Higher Strike Put (ATM/ITM).
Example: Buy Nifty 24,800 PE. - Sell a Lower Strike Put (OTM).
Example: Sell Nifty 24,400 PE. - Net Premium Paid = Premium of Long Put – Premium of Short Put.
Formulas:
- Max Profit = (Higher Strike – Lower Strike) – Net Premium Paid
- Max Loss = Net Premium Paid
- Breakeven Point = Higher Strike – Net Premium Paid
4. Bear Put Spread Example with Numbers
Let’s take an example with Reliance Industries:
- Current Price: ₹2,500
- Buy 2500 PE @ ₹80
- Sell 2400 PE @ ₹30
- Net Premium Paid = ₹80 – ₹30 = ₹50 (₹5,000 for 100 shares lot)
Scenarios at Expiry
Case 1: Stock above ₹2,500
- Both options expire worthless.
- Loss = Net Premium Paid = ₹5,000
- Max Loss = ₹5,000
Case 2: Stock at ₹2,450
- 2500 PE = Intrinsic Value = ₹50 (₹5,000)
- 2400 PE = 0
- Net = ₹5,000 – ₹5,000 = Breakeven
Case 3: Stock at ₹2,400
- 2500 PE = ₹100 (₹10,000)
- 2400 PE = 0
- Net = ₹10,000 – ₹5,000 = ₹5,000 profit
Case 4: Stock at ₹2,350
- 2500 PE = ₹150 (₹15,000)
- 2400 PE = ₹50 (₹5,000)
- Net = ₹10,000 – ₹5,000 = ₹5,000 (profit capped)
✅ Max Profit = ₹5,000
✅ Max Loss = ₹5,000
5. Payoff Analysis
The payoff structure of a Bear Put Spread is:
- Maximum Profit: Limited (difference between strikes – net premium).
- Maximum Loss: Limited (net premium paid).
- Breakeven Point: Higher strike – net premium.
It provides a defined risk/reward profile – ideal for conservative bearish traders.
6. Advantages of Bear Put Spread
- Lower Cost than Naked Put: Selling the lower strike reduces premium.
- Defined Risk: You know your maximum loss upfront.
- Suitable for Moderate Bearish View: Works best when downside is limited.
- Hedging Tool: Can hedge long stock positions against mild declines.
7. Risks/Disadvantages
- Limited Profit: Gains are capped even if stock falls heavily.
- Time Decay: Premium erodes if stock doesn’t move down quickly.
- Correct Timing Required: Needs a fall before expiry, otherwise loss occurs.
- Opportunity Cost: If stock crashes, naked put would earn more.
8. Bear Put Spread vs Other Strategies
| Strategy | Risk | Reward | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Naked Put Buy | Limited (premium) | Unlimited (stock to zero) | Strong bearish view |
| Bear Put Spread | Limited | Limited | Moderate bearish outlook |
| Short Call Spread | Limited | Limited | Bearish outlook via calls |
| Protective Put | Premium cost | Unlimited downside protection | Hedging long stock |
9. Real-World Example (Nifty)
Suppose Nifty is trading at 24,800.
- Buy 24,800 PE @ 200
- Sell 24,400 PE @ 100
- Net Premium Paid = ₹100 (₹5,000 for lot size 50)
Expiry Scenarios
- Nifty above 24,800 → Loss = ₹5,000 (Max Loss)
- Nifty at 24,600 → Profit = ₹10,000 – ₹5,000 = Breakeven
- Nifty at 24,400 or below → Max Profit = (24,800 – 24,400 – 100) × 50 = ₹15,000
✅ Works well when Nifty is expected to decline moderately.
10. Tips for Traders
- Pick strikes wisely → Higher strike should be near current price, lower strike at expected support.
- Use in stable bearish moves → Avoid in extremely volatile markets.
- Use short expiries → For better cost efficiency and faster results.
- Don’t expect unlimited gains → This is a conservative bearish trade.
11. Who Should Use Bear Put Spreads?
- Beginner option traders (safer than naked puts).
- Retail investors with limited capital.
- Traders with moderate bearish views.
- Conservative players who prefer defined risk.
12. Conclusion
The Bear Put Spread is an effective strategy for traders who expect a moderate decline in a stock or index. By buying a higher strike put and selling a lower strike put, you reduce premium costs and define both your risk and reward.
Yes, profit is capped, but this trade-off makes it suitable for conservative traders and beginners. In practical terms, it’s a cost-efficient bearish strategy that balances risk with return.
For anyone looking to build a well-rounded options trading toolkit, the Bear Put Spread deserves a place alongside strategies like the Covered Call, Bull Call Spread, and Protective Put.
13. FAQs
Q1: What is the maximum profit in a Bear Put Spread?
👉 Max profit = Difference between strikes – Net premium paid.
Q2: What is the maximum loss?
👉 Max loss = Net premium paid.
Q3: Is Bear Put Spread good for beginners?
👉 Yes, it’s safer than buying a naked put.
Q4: Can it be used on indices like Nifty/Bank Nifty?
👉 Absolutely, it’s widely used for index trading.
Q5: How is it different from a naked put buy?
👉 Bear Put Spread is cheaper but has capped profit; naked put is costlier but unlimited profit potential.
✅ Key Takeaway:
Bear Put Spread = Buy higher strike put + Sell lower strike put = Limited risk, limited reward, best for moderately bearish markets.
📌Disclaimer – At BullBearFin, we don’t provide trading tips but focus on helping you understand financial markets better so you can make informed decisions.

Post Comment